Irrational behaviors in financial investment are a common occurrence among investors, regardless of their experience or expertise. These behaviors can have a significant impact on investment decisions and outcomes, often leading to poor financial results. Understanding and recognizing these irrational behaviors is crucial for investors to make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes.

1.Herd Mentality
One of the most prevalent irrational behaviors in financial investment is herd mentality. This occurs when investors follow the crowd and make investment decisions based on the actions of others, rather than conducting their own research and analysis. Herd mentality can lead to the formation of investment bubbles, where asset prices become detached from their intrinsic value. When these bubbles burst, investors who followed the herd suffer significant losses.

2.Overconfidence
Another irrational behavior is overconfidence. Many investors believe they have superior knowledge or skills that give them an edge in the market. This overconfidence often leads to excessive trading and a failure to properly diversify investments. Overconfident investors may also ignore or downplay risks, leading to poor decision-making and potential financial losses.
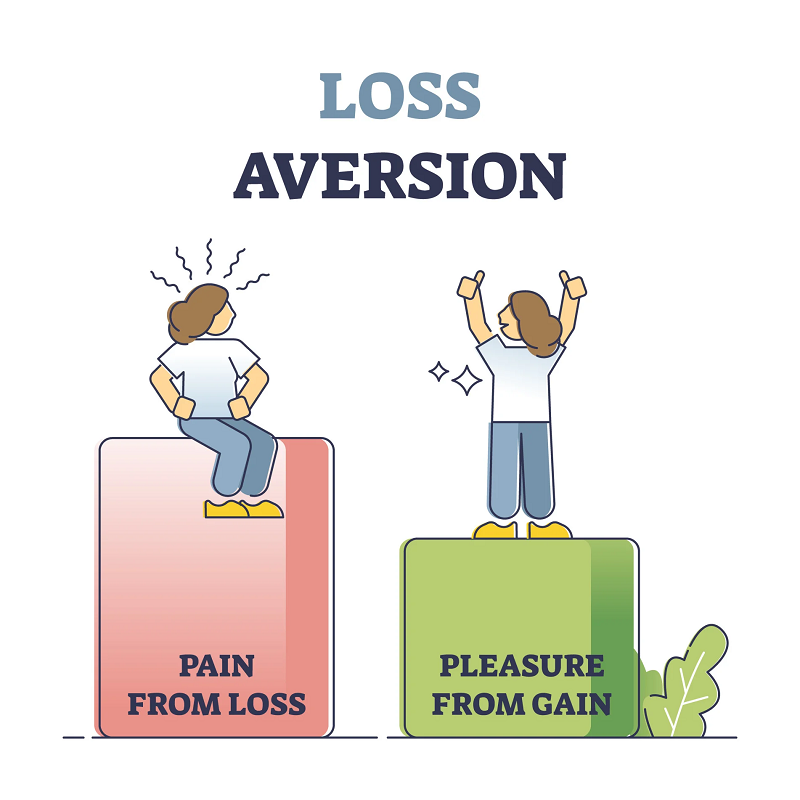
3.Loss Aversion Loss aversion is another common irrational behavior in financial investment. Investors tend to feel the pain of losses more strongly than the pleasure of gains. This leads to a reluctance to sell losing investments, as investors hope that the market will eventually turn in their favor. This behavior can result in holding onto underperforming assets for too long, missing out on potential gains from other investment opportunities.
4.Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias is another irrational behavior that affects investment decision-making. Investors have a tendency to seek out information that confirms their existing beliefs or opinions, while ignoring or discounting information that contradicts them. This bias can lead to a narrow and biased view of the market, preventing investors from considering alternative perspectives and potentially missing out on valuable insights.

5. Anchoring Bias
Another irrational behavior is anchoring bias. This occurs when investors rely too heavily on a particular piece of information or reference point when making investment decisions. For example, investors may anchor their expectations for future returns based on past performance or the initial purchase price of an asset. This bias can lead to a failure to adjust investment strategies in response to changing market conditions, resulting in missed opportunities or excessive risk-taking.

6.Impulsivity
Impulsivity is another irrational behavior that can have a detrimental impact on investment outcomes. Many investors make impulsive decisions based on short-term market fluctuations or emotional reactions, rather than considering long-term investment goals and strategies. Impulsive investors may buy or sell assets without proper analysis or consideration of the potential consequences, leading to poor investment performance.
7.Recency Bias
Lastly, recency bias is another common irrational behavior in financial investment. Investors often give more weight to recent events or trends when making investment decisions, while ignoring or discounting historical data or longer-term trends. This bias can lead to a failure to properly assess risks and opportunities, as well as a tendency to chase after short-term market trends rather than adopting a disciplined and long-term approach.
In conclusion, irrational behaviors in financial investment are prevalent among investors and can have a significant impact on investment outcomes. Recognizing and understanding these behaviors is essential for investors to make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes. By adopting a disciplined and rational approach to investing, investors can improve their chances of achieving their financial goals and avoiding the pitfalls of irrational decision-making.