Green finance is the provision of financial services and products that support the transition to a low-carbon, sustainable, and resilient economy. Green finance can help address the challenges and opportunities of climate change, environmental degradation, and natural resource depletion, by mobilizing and allocating capital for green projects, activities, and sectors. Green finance can also help promote green sustainable development, which is the development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
The role and promotion of green finance on sustainable development can be discussed from different perspectives, such as:
The global perspective: Green finance can contribute to the achievement of the global goals and commitments on sustainable development, such as the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the Paris Agreement on Climate Change, and the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction. Green finance can help align the financial system with the environmental and social dimensions of sustainable development, and foster international cooperation and coordination on green finance issues and initiatives. For example, the UNEP Inquiry into the Design of a Sustainable Financial System was launched in 2014 to explore how the financial system can be reformed to support the transition to a green economy. The Network for Greening the Financial System was established in 2017 to enhance the role of central banks and supervisors in addressing climate-related and environmental risks. The Green Bond Principles were developed in 2014 to provide voluntary guidelines for the issuance of green bonds, which are debt instruments that finance green projects and activities.
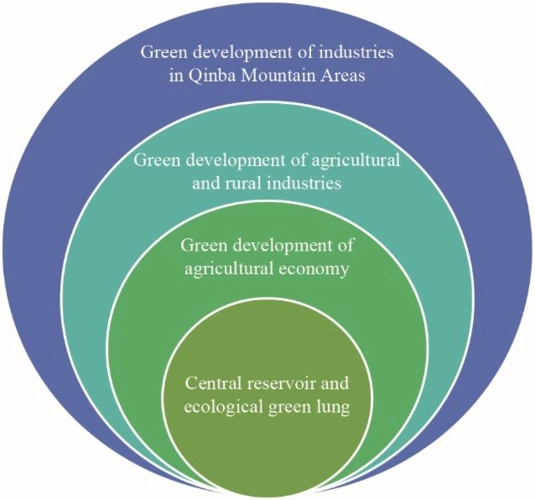
The national perspective: Green finance can support the implementation of the national policies and strategies on sustainable development, such as the national development plans, the nationally determined contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement, and the national adaptation plans (NAPs). Green finance can help mobilize and allocate domestic and foreign resources for green investments, and create enabling conditions and incentives for green growth and innovation. For example, China has been a pioneer and leader in green finance, with a comprehensive policy framework and a large market for green financial products and services. China issued its Guidelines for Establishing the Green Financial System in 2016, which cover various aspects of green finance, such as green credit, green bonds, green insurance, green funds, and green ratings. China also launched its National Green Development Fund in 2020, which aims to provide equity financing for green projects and enterprises.
The local perspective: Green finance can facilitate the integration of environmental and social considerations into the decision-making and operations of local actors, such as subnational governments, financial institutions, corporations, and households. Green finance can help address the local challenges and opportunities of sustainable development, such as urbanization, pollution, biodiversity, and social inclusion. Green finance can also help empower and engage the local stakeholders and communities in the transition to a green economy. For example, [India] has been promoting green finance at the local level, with various initiatives and innovations, such as green municipal bonds, green microfinance, green crowdfunding, and green social enterprises. India issued its first [green municipal bond] in 2017, which raised funds for renewable energy and energy efficiency projects in the city of Pune. India also launched its [Green Window] in 2020, which is a dedicated financing platform for green and inclusive energy solutions for the underserved segments of the population.