Governance and regulation of financial institutions is a topic that involves the principles, rules, and practices that guide and oversee the conduct and performance of financial institutions, such as banks, insurance companies, and other entities that provide financial services. Governance and regulation of financial institutions aim to ensure the soundness, stability, and efficiency of the financial system, as well as to protect the interests and rights of various stakeholders, such as shareholders, creditors, customers, regulators, and the public.
According to the web search results that I found using the query “Governance and regulation of financial institutions”, here are some of the main points and insights that I can share with you:
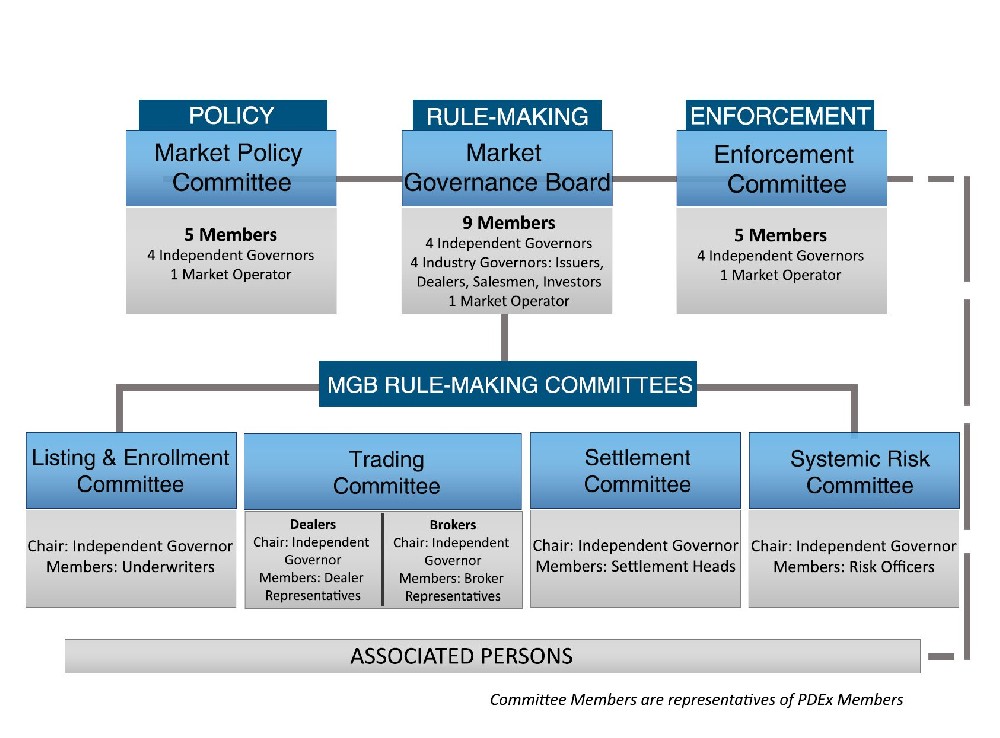
Governance and regulation of financial institutions are closely related, but not identical concepts. Governance refers to the internal mechanisms and structures that financial institutions use to direct and control their activities, such as the board of directors, the management, the risk management, the internal audit, and the compliance functions. Regulation refers to the external rules and standards that financial institutions have to comply with, such as the laws, regulations, and guidelines issued by the authorities, such as the central bank, the prudential supervisor, the market regulator, and the deposit insurance agency.
Governance and regulation of financial institutions are influenced by various factors, such as the economic theory, the supervisory practice, the empirical evidence, and the policy objectives. Different theories and models have been developed to explain and evaluate the governance and regulation of financial institutions, such as the agency theory, the stakeholder theory, the market discipline theory, and the public interest theory. Different practices and approaches have been adopted by different countries and regions, such as the Basel framework, the European Union directives, and the US Dodd-Frank Act. Different evidence and data have been collected and analyzed to assess the impact and effectiveness of governance and regulation of financial institutions, such as the performance, the risk, the stability, and the innovation indicators. Different objectives and priorities have been pursued and balanced by different actors and institutions, such as the profitability, the safety, the competition, and the social responsibility goals.
Governance and regulation of financial institutions are subject to ongoing challenges and changes, both for the financial institutions themselves and for the regulators and supervisors. Some of the challenges and changes include the complexity and uncertainty of the rules, the potential for regulatory arbitrage and capture, the unintended consequences for market efficiency and innovation, the lack of coordination and cooperation among global regulators, the emergence of new risks and opportunities, such as the fintech and the digital currencies, and the integration of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors.