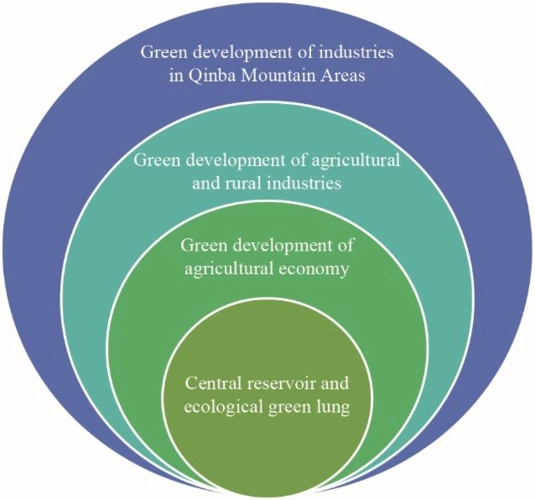
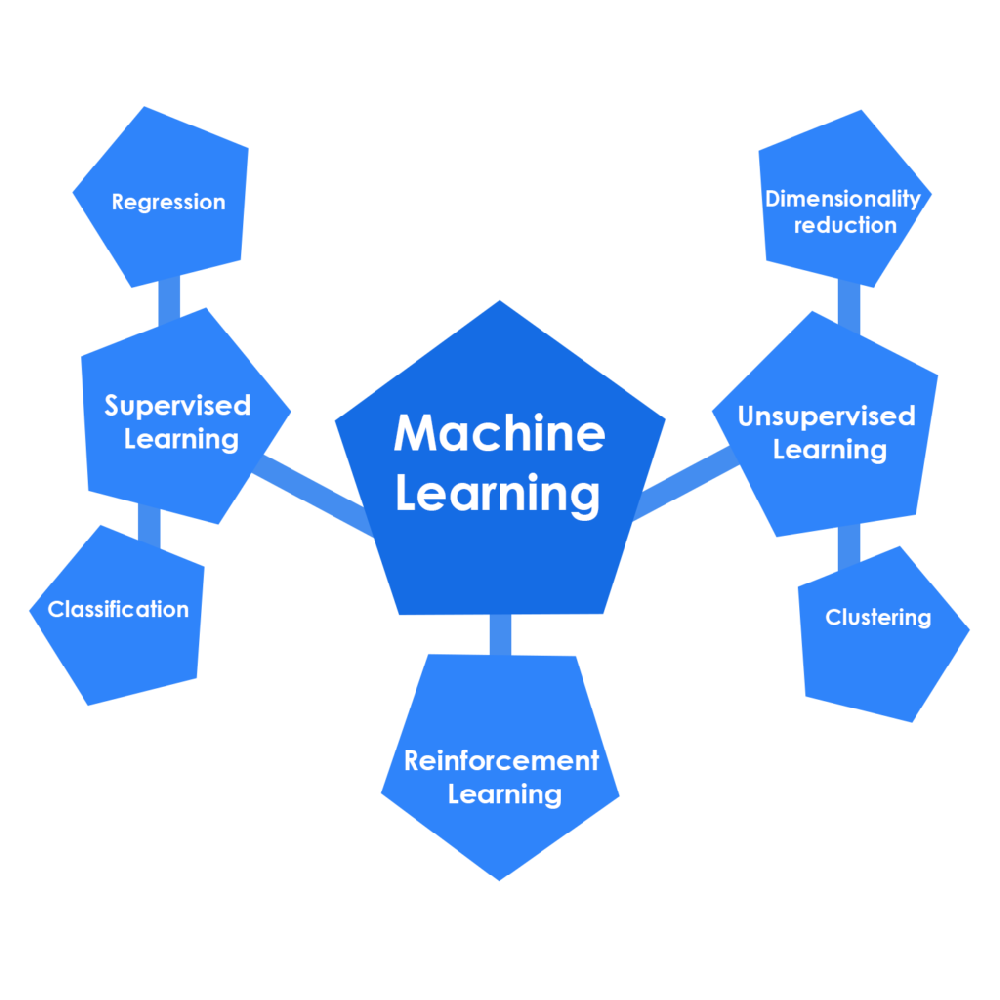
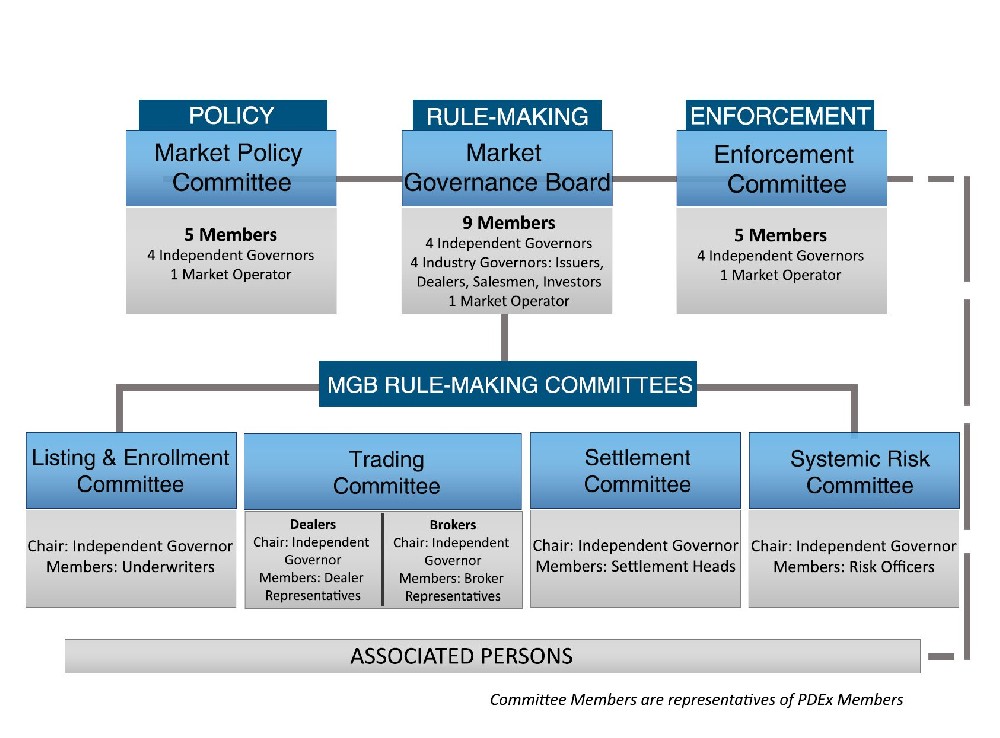
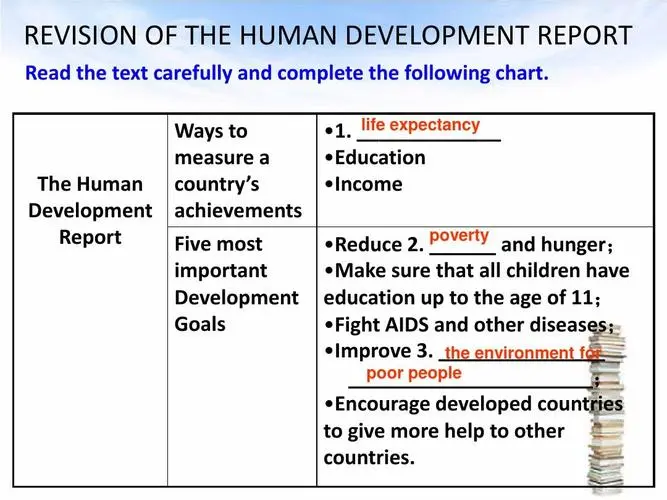
The operating mechanism and influence of financial markets is a broad and complex topic that involves many aspects of economics, finance, and business. However, I will try to give you a brief overview based on the web search results I found.
Financial markets are places where people buy and sell financial instruments, such as stocks, bonds, currencies, and derivatives. Financial markets play a vital role in facilitating the smooth operation of capitalist economies by allocating resources and creating liquidity for businesses and entrepreneurs1. Financial markets also enable investors to search for returns and diversify their risks.
The operating mechanism of financial markets depends on the types and classes of instruments available, the rules and regulations that govern the transactions, the information and transparency of the market participants, and the supply and demand of the financial assets. Some financial markets are highly organized and regulated, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or the Nasdaq, while others are more informal and decentralized, such as the over-the-counter (OTC) market or the foreign exchange (forex) market.
The influence of financial markets on countries’ economic life is significant and multifaceted. Financial markets affect the economy through various channels, such as:
Monetary policy: Governments can influence the money supply and the interest rates in the economy by conducting open market operations, changing the reserve requirements, or adjusting the discount rate. These actions affect the availability and cost of credit, which in turn affect the investment, consumption, and saving decisions of households and firms.
Currency and inflation: Governments can also influence the value of their currencies by intervening in the foreign exchange market, either directly or indirectly. A change in the exchange rate affects the competitiveness of exports and imports, the purchasing power of consumers and producers, and the inflation rate in the economy.
Market failures and bailouts: Sometimes, financial markets may fail to allocate resources efficiently or to reflect the true value of the assets. This can lead to market bubbles, crashes, or crises, which can have severe consequences for the financial system and the real economy. In such cases, governments may intervene to stabilize the markets, regulate the transactions, provide institutional frameworks, and enforce rules around contract law and property rights. Governments may also provide bailouts or emergency measures to support failing companies or sectors that are deemed too big or too important to fail.
Subsidies and tariffs: Governments can also influence the markets by creating subsidies or tariffs, which are forms of government intervention that affect the prices and quantities of goods and services. Subsidies are payments from the government to an industry or a producer, which lower the cost of production and increase the supply. Tariffs are taxes imposed on imported goods, which raise the price of imports and reduce the demand. Subsidies and tariffs can be used to protect domestic industries, promote social welfare, or achieve political goals.
Taxes, fees, and regulations: Governments can also influence the markets by imposing taxes, fees, and regulations on various activities, transactions, or industries. These can affect the profitability, competitiveness, and innovation of businesses, as well as the incentives, behavior, and welfare of consumers. Taxes, fees, and regulations can be used to generate revenue, correct externalities, redistribute income, or achieve other policy objectives.
As you can see, financial markets are influenced by many factors and have a significant impact on countries’ economic life.