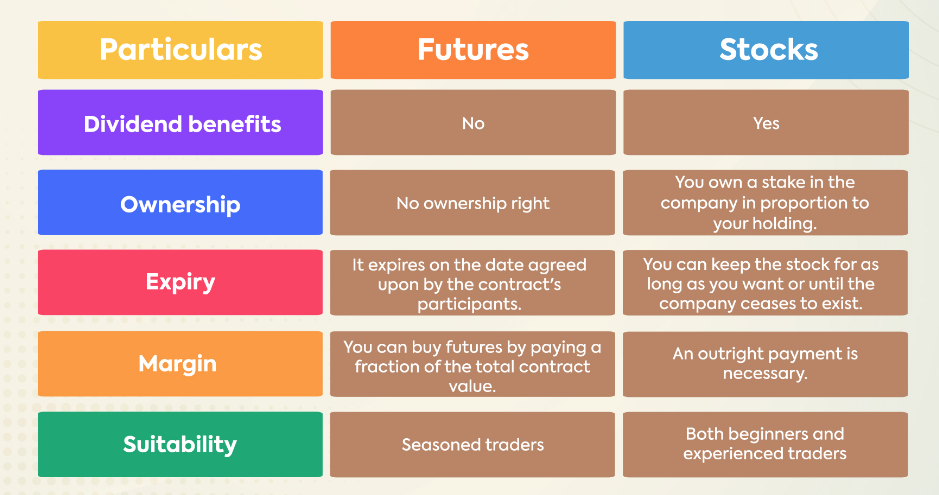
Futures and stocks are different types of financial assets that have different characteristics, risks, and rewards. Here are some of the main differences between them:
Futures are contracts that oblige the buyer and seller to exchange an asset at a predetermined price and date in the future. Stocks are shares of ownership in a company that entitle the holder to a portion of its profits and assets.
Futures are standardized and traded on organized exchanges, while stocks can vary in size, quality, and features, and are traded on various markets.
Futures have expiration dates, while stocks do not. Futures contracts need to be closed or rolled over before they expire, while stocks can be held indefinitely.
Futures use leverage, which means that traders can control a large amount of the underlying asset with a small amount of money. Stocks require full payment of the purchase price, unless the trader uses margin borrowing, which is limited and regulated.
Futures are mainly used for hedging, speculation, or arbitrage, while stocks are mainly used for investing, income, or growth.
You can learn more about the differences between futures and stocks from the web search results I found for you.
As for the theory that is suitable for beginners, there is no definitive answer, as different theories may suit different investors depending on their goals, preferences, and risk tolerance. However, some of the common theories that beginners may find useful are:
Fundamental analysis, which is the method of evaluating the intrinsic value of a stock based on its financial performance, competitive advantage, growth potential, and other factors.
Behavioral finance, which is the study of how psychological factors, such as emotions, biases, and heuristics, affect the decision-making and behavior of investors.